-
.Net
-
Backup
-
Data Storage Containers
-
Docker Containers
-
Environment Management
- Swap-Domains
- Clone Environment
- Create Environment
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Migration between Regions
- Environment Regions
- Environment Transferring
- Environment Variable
- Environment Variables
- Environment Variables(Apache meaven, Memcached)
- Environment Variables(Go)
- Environment Variables(JAVA)
- Environment Variables(Load Balancer)
- Environment Variables(Node.js)
- Environment Variables(PHP)
- Environment Variables(Ruby)
- How to Migrate a WordPress Site to BitssCloud PaaS
- How to migrate my environments from another Jelastic provider?
- HTTP Headers
- Java VCS Deployment with Maven
- Setting Up Environment
- Share Environment
- Why is my environment in sleeping mode?
- Show all articles (9) Collapse Articles
-
Java
- Environment Variables - Java custom Environment Variables
- Java App server Configuration
- Java Options and Arguments
- Multiple Domains on Tomcat server
- Secure Java Encryption and Decryption
- Spring Boot Standalone and Clustered Java Applications with BitssCloud
- Timezone Data for Java/PHP App Server
- Tomcat HTTP to HTTPS redirect
- WildFly server
-
LiteSpeed Web Server
-
OOM Killer
-
Python
-
Reseller SetUp
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
-
Troubleshooting
-
Account Management
-
CDN
-
Databases
- Database Configuration
- Database Connection Strings
- Database Hosting in BitssCloud
- Environment Variables(Database)
- Galera Cluster not working
- How to export/Import Database via Command line
- How to install MSSQL server on Linux (2017)
- MariaDB/MySQL Auto-Сlustering
- MongoDB Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Replication
- PostgreSQL Master-Slave Cluster
- Remote Access to PostgreSQL
- Schedule Backups for MySQL and MariaDB Databases
- Scheduling Databases Backups
-
Domain Name Management
- Container Redeploy
- Custom Domain Name
- DNS Hostnames for Direct Connection to Containers
- How to Bind Custom Domain via A Record
- How to Bind Custom Domain via CNAME
- Multiple Custom Domains on an Nginx Web Server
- Multiple Domains with Public IP
- Multiple Public IP Addresses for a Single Container
- Setup WordPress Multisite Network with Domain Mapping and CDN
-
Jenkins
-
Load Balancing
-
PHP
- Creating Environment for PHP
- Deploy PHP Project Via GIT SVN
- How to Check Change PHP Version in BitssCloud
- How to create environment for AngularJs/ReactJs
- How to Enable PHP Extensions
- How to Install Custom PHP Application
- Ion cube Loader
- MariaDB PHP connection
- MySQL PHP Connection
- NGINX PHP
- PHP App Server Configuration
- PHP Connection to MongoDB
- PHP security settings
- PHP Session Clustering
- PostgreSQL PHP Connection
- Running Multiple Domain Names on Apache Server
- Security configuration for Apache
- Zero Downtime (ZDT) Deployment for PHP
- Show all articles (3) Collapse Articles
-
Release Notes
-
Ruby
-
SSH
-
Wordpress
-
Application Management
-
Cluster
-
Deploying Projects
-
Elastic VPS
- CentOS VPS
- Elastic VPS configuratation
- Elastic VPS with full root access
- Installation of cPanel in BitssCloud
- Java Console Application with CentOS VPS
- Linux VPS Access via Public IP
- Linux VPS Access via SSH Gate
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- SSH Access to VPS Gate
- Ubuntu VPS
- Ubuntu with CSF Firewall
-
High Availability
-
Jitsi
-
Node.js
-
Pricing System
-
Request Handling
-
Scaling
- Application Server with horizontal scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling: Multi Nodes
- Automatic Vertical Scaling
- Database Horizontal Scaling
- Docker Containers Horizontal Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
- Load Balancer with horizontal scaling
- Memcached horizontal scaling
- Storage Container
- VPS Horizontal Scaling
-
Traffic Distributor
-
General
- Apache & NGINX Modules
- BitssCloud Dashboard Guide
- Build and Deploy Hooks
- Cron Job scheduler
- FFMPEG Setup
- File Synchronization
- FTP Overview
- FTP/FTPS Support in BitssCloud
- How to Deploy Magento into BitssCloud PHP Cloud
- How to Enable Expert Mode in JCA
- How to open a support ticket to BitssCloud
- Installation of FTP
- Kubernetes Cluster
- MarketPlace
- Reduce Cloud Waste with Automatically Scheduled Hibernation
- Run Configuration
- SFTP Protocols for Accessing BitssCloud Containers.
- Supported OS Distributions for Docker Containers
- Timezone Addon
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Types of Accounts
- Varnish
- Websockets Support
- What is Cloudlet
- What is PaaS & CaaS
- WordPress AddOn
- Zero Code Change Deploy with No Vendor Lock-In for Smooth Migration across Cloud Platforms
- Show all articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
Go lang
-
Wordpress category
-
Data Storage Container
-
Memcached
-
Account & Pricing
Environment Variables – Java custom Environment Variables
Environment variables represent a kind of placeholders, where you can store the frequently used parameters’ values or strings in order not to specify them manually in the code each time they are needed. There is a number of default environment variables that are preconfigured at BitssCloud application servers and can be easily integrated into your app, hosted within these servers, to make your work with BitssCloud even more convenient. The following guide will acquaint you with the details on how to add your custom environment variables to particular Java application servers: 1. Tomcat 6, 7, TomEE or Jetty2. GlassFish 3
Note that the same operations can be done by means of establishing the SSH connection to any of your servers and declaring variables in the corresponding configuration file via console.
1. Tomcat 6, 7, TomEE and Jetty Variables
The following workflow is pretty simple and identical to the majority of supported Java application servers, so let’s check it out first.
1. Click the Config button for your application server (Tomcat 6, 7, TomEE, or Jetty).
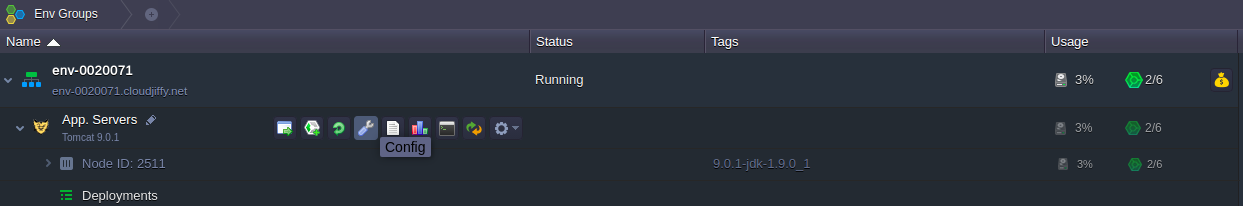
2. In the opened tab, navigate to the /opt/tomcat/conf directory and choose the variables.conf file within it. There you’ll see a short instruction on setting your custom environment variables.
Follow it, by means of adding the desired custom variables here. Each variable should be either separated by a space from the next one or started from a new line.For example:
-Dvar1=value1 -Dvar2=value2
-Dmy.var3=/my/value

| Note: you can also set JVM options in this file. As an example, you can see the Garbage Collection agent option declared just above the circled area at the image. |
Do not forget to Save the configurations you’ve made.
3. Then make the appropriate changes in your application’s code with the help of the System.getProperty(“your_variable”) method to appoint the specified values to the needed arguments.For example:
String var1 = System.getProperty(“var1”);
String var2 = System.getProperty(“var2”);
String var3 = System.getProperty(“var3“)
4. Once this is completed, Restart your application server using the corresponding button next to it.
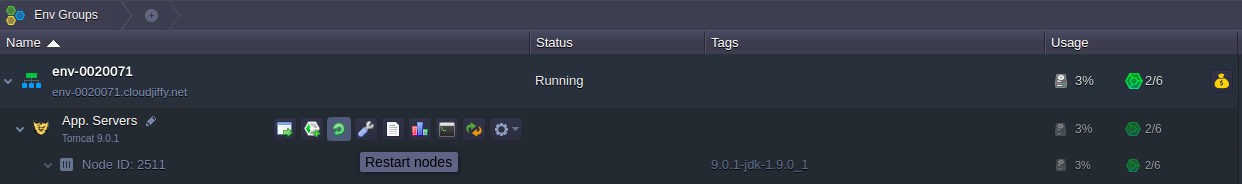
As a result, all the newly stated configurations will be applied.2. GlassFish 3 Variables
For Glassfish, variables configuration is performed through its Administration Console so the process will be the following:
1. Click the last button (with the gear icon) for GlassFish in your environment and choose Admin panel > Login in the appeared list (or follow the link to the Admin console which you’ve received via email after environment creation).
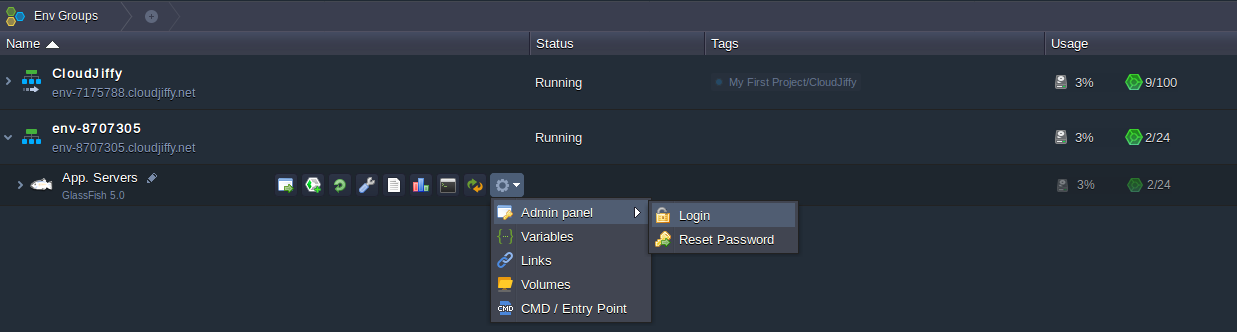
2. Fill in the Username and Password fields with the credentials from the same email received earlier.

3. Once inside, choose the gfcluster-config > JVM Settings option within the Configuration’s section at the left-hand menu list.
4. Then select the JVM Options tab and click on the Add JVM Option button above the Options list. A new empty field will appear at the top of the list, wherein you can enter your custom environment variable (e.g. -Dvar1=value1).

If you’d like to call a JAR file as the option’s argument, just upload it to the home folder of your GlassFish server and specify the path to it for the desired option, for example:-javaagent:/opt/glassfish3/temp/newrelic.jar

After all the desired parameters are set, click the Save button.
5. If everything is OK, you’ll get the next message:

6. Finally, switch back to your BitssCloud dashboard and restart GlassFish using the corresponding button.
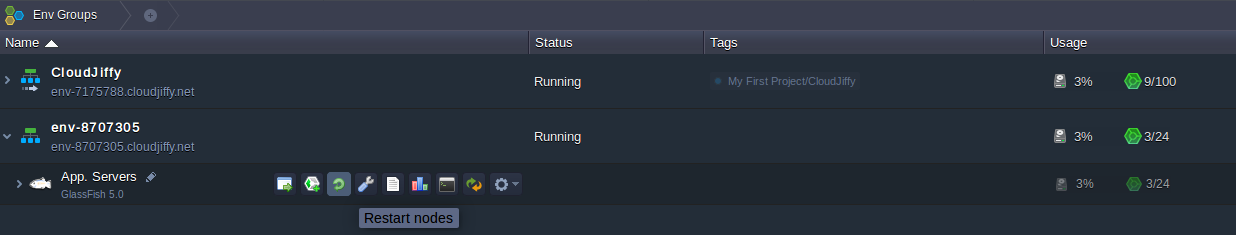
That’s all. In such away, you can manage GlassFish environment variables through the Admin Console.
