-
.Net
-
Backup
-
Data Storage Containers
-
Docker Containers
-
Environment Management
- Swap-Domains
- Clone Environment
- Create Environment
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Migration between Regions
- Environment Regions
- Environment Transferring
- Environment Variable
- Environment Variables
- Environment Variables(Apache meaven, Memcached)
- Environment Variables(Go)
- Environment Variables(JAVA)
- Environment Variables(Load Balancer)
- Environment Variables(Node.js)
- Environment Variables(PHP)
- Environment Variables(Ruby)
- How to Migrate a WordPress Site to BitssCloud PaaS
- How to migrate my environments from another Jelastic provider?
- HTTP Headers
- Java VCS Deployment with Maven
- Setting Up Environment
- Share Environment
- Why is my environment in sleeping mode?
- Show all articles (9) Collapse Articles
-
Java
- Environment Variables - Java custom Environment Variables
- Java App server Configuration
- Java Options and Arguments
- Multiple Domains on Tomcat server
- Secure Java Encryption and Decryption
- Spring Boot Standalone and Clustered Java Applications with BitssCloud
- Timezone Data for Java/PHP App Server
- Tomcat HTTP to HTTPS redirect
- WildFly server
-
LiteSpeed Web Server
-
OOM Killer
-
Python
-
Reseller SetUp
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
-
Troubleshooting
-
Account Management
-
CDN
-
Databases
- Database Configuration
- Database Connection Strings
- Database Hosting in BitssCloud
- Environment Variables(Database)
- Galera Cluster not working
- How to export/Import Database via Command line
- How to install MSSQL server on Linux (2017)
- MariaDB/MySQL Auto-Сlustering
- MongoDB Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Replication
- PostgreSQL Master-Slave Cluster
- Remote Access to PostgreSQL
- Schedule Backups for MySQL and MariaDB Databases
- Scheduling Databases Backups
-
Domain Name Management
- Container Redeploy
- Custom Domain Name
- DNS Hostnames for Direct Connection to Containers
- How to Bind Custom Domain via A Record
- How to Bind Custom Domain via CNAME
- Multiple Custom Domains on an Nginx Web Server
- Multiple Domains with Public IP
- Multiple Public IP Addresses for a Single Container
- Setup WordPress Multisite Network with Domain Mapping and CDN
-
Jenkins
-
Load Balancing
-
PHP
- Creating Environment for PHP
- Deploy PHP Project Via GIT SVN
- How to Check Change PHP Version in BitssCloud
- How to create environment for AngularJs/ReactJs
- How to Enable PHP Extensions
- How to Install Custom PHP Application
- Ion cube Loader
- MariaDB PHP connection
- MySQL PHP Connection
- NGINX PHP
- PHP App Server Configuration
- PHP Connection to MongoDB
- PHP security settings
- PHP Session Clustering
- PostgreSQL PHP Connection
- Running Multiple Domain Names on Apache Server
- Security configuration for Apache
- Zero Downtime (ZDT) Deployment for PHP
- Show all articles (3) Collapse Articles
-
Release Notes
-
Ruby
-
SSH
-
Wordpress
-
Application Management
-
Cluster
-
Deploying Projects
-
Elastic VPS
- CentOS VPS
- Elastic VPS configuratation
- Elastic VPS with full root access
- Installation of cPanel in BitssCloud
- Java Console Application with CentOS VPS
- Linux VPS Access via Public IP
- Linux VPS Access via SSH Gate
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- SSH Access to VPS Gate
- Ubuntu VPS
- Ubuntu with CSF Firewall
-
High Availability
-
Jitsi
-
Node.js
-
Pricing System
-
Request Handling
-
Scaling
- Application Server with horizontal scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling: Multi Nodes
- Automatic Vertical Scaling
- Database Horizontal Scaling
- Docker Containers Horizontal Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
- Load Balancer with horizontal scaling
- Memcached horizontal scaling
- Storage Container
- VPS Horizontal Scaling
-
Traffic Distributor
-
General
- Apache & NGINX Modules
- BitssCloud Dashboard Guide
- Build and Deploy Hooks
- Cron Job scheduler
- FFMPEG Setup
- File Synchronization
- FTP Overview
- FTP/FTPS Support in BitssCloud
- How to Deploy Magento into BitssCloud PHP Cloud
- How to Enable Expert Mode in JCA
- How to open a support ticket to BitssCloud
- Installation of FTP
- Kubernetes Cluster
- MarketPlace
- Reduce Cloud Waste with Automatically Scheduled Hibernation
- Run Configuration
- SFTP Protocols for Accessing BitssCloud Containers.
- Supported OS Distributions for Docker Containers
- Timezone Addon
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Types of Accounts
- Varnish
- Websockets Support
- What is Cloudlet
- What is PaaS & CaaS
- WordPress AddOn
- Zero Code Change Deploy with No Vendor Lock-In for Smooth Migration across Cloud Platforms
- Show all articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
Go lang
-
Wordpress category
-
Data Storage Container
-
Memcached
-
Account & Pricing
Load Alerts
While creating an environment, you state the cloudlet limits for each node. In such a way, the resources are limited and the spending are regulated. When the traffic grows an application requests more resources for normal work. And, if the limits created by you are too low, this can lead to failure in-app performance.
To monitor your application’s load and the number of resources it requires, you can configure a set of automatic notification triggers. They are executed if the usage of a particular resource type is above/below the stated value (%) during the appropriate time period. As a result, you’ll get an email notification about your application’s load change.
- Triggers Execution History
Create Alert
In order to configure an alert, follow the next instruction:
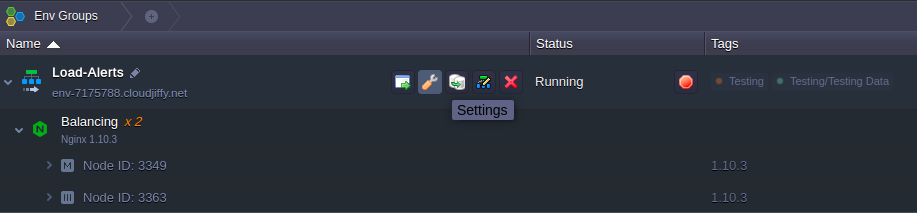
1. Click the Settings button for the desired environment:
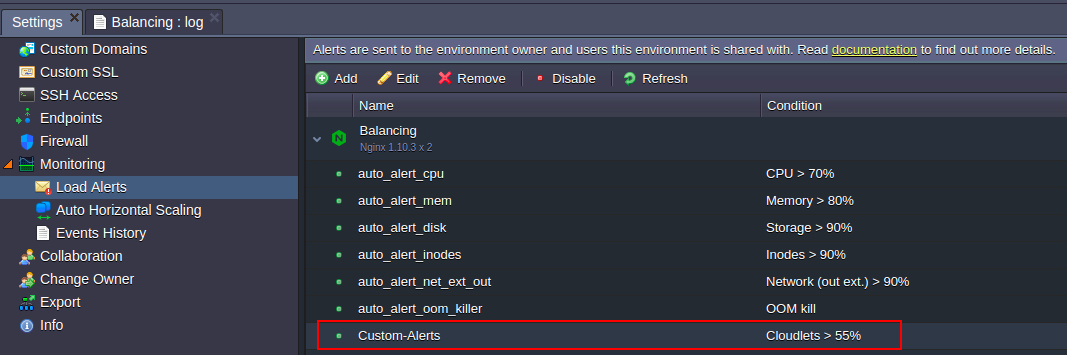
2. In the opened tab, navigate to the Monitoring > Load Alerts section:
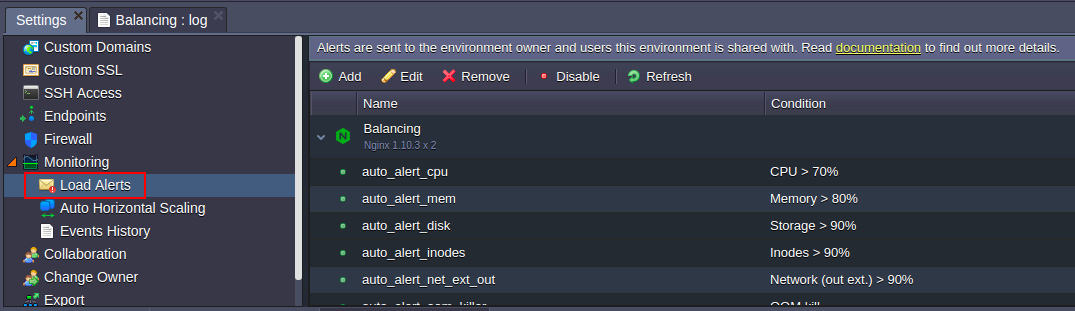
Here, if such is stated within your hosting service provider’s settings, you can find a bunch of default triggers, which are automatically added during environment creation. These ones, if exist, are to notify you when the RAM, CPU, disk, inodes or network traffic usage at any node is coming close to current resource limits (according to the predefined by hoster levels of consumption for notification).
3. Using the buttons in the tool panel, you can either Add a new alert or Edit, Remove, Enable/Disablethe already existing ones (including the default triggers set). Also, alerts list can be Refreshed using the corresponding button.
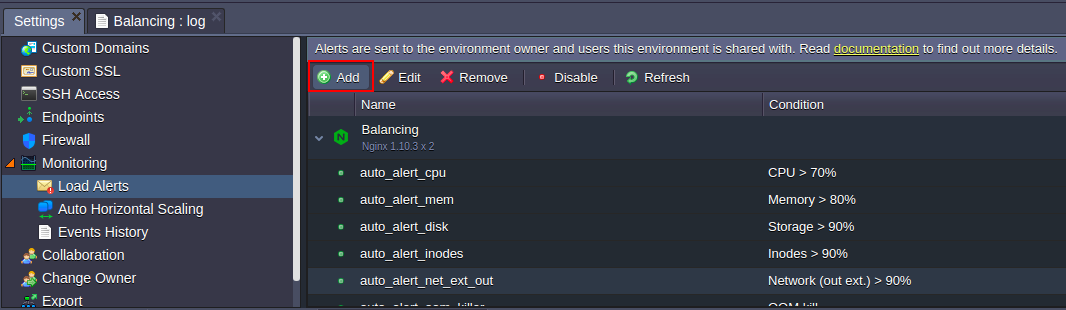
Let’s consider a case of setting up your own trigger – for that, click on the Add button, circled in the image above.4. In the opened Add alert frame, define the following values:
- Name – name of the notification trigger
- Nodes – type of the environment’s node (you can apply trigger to any node within the chosen environment)
- Whenever – type of resources that will be monitored by trigger: Cloudlets (Memory, CPU), Memory, CPU, Network (out ext. + in ext.), Network (out ext.), Storage (disk space amount), Disk I/O, Disk IOPS and Inodes
- Is – condition for trigger invocation/execution, due to which the resource consumption should be above or below (the “>” or “<” values correspondingly – use the first combo-box) of the stated percentage or Mbps for the Network monitoring
- For at least – time period before trigger execution, during which it should remains invoked
- Notification frequency – delay for the repetitive message to be sent
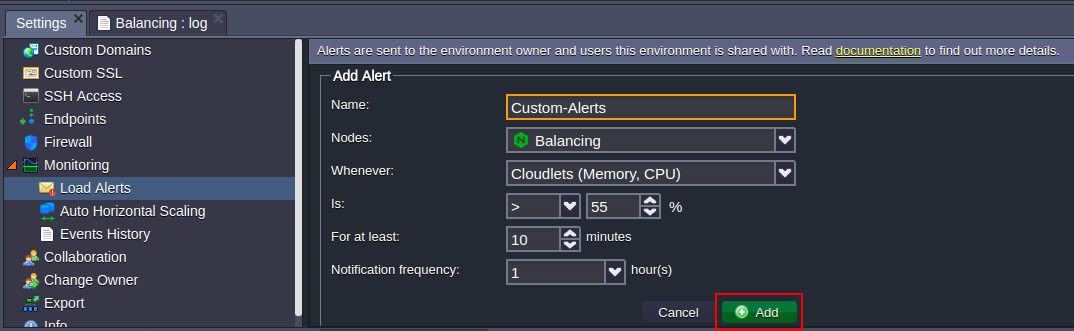
After you’ve stated all the preferable configurations, click Add button.
5. As soon as alert is configured and activated, it will appear within list with the name.