-
.Net
-
Backup
-
Data Storage Containers
-
Docker Containers
-
Environment Management
- Swap-Domains
- Clone Environment
- Create Environment
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Migration between Regions
- Environment Regions
- Environment Transferring
- Environment Variable
- Environment Variables
- Environment Variables(Apache meaven, Memcached)
- Environment Variables(Go)
- Environment Variables(JAVA)
- Environment Variables(Load Balancer)
- Environment Variables(Node.js)
- Environment Variables(PHP)
- Environment Variables(Ruby)
- How to Migrate a WordPress Site to BitssCloud PaaS
- How to migrate my environments from another Jelastic provider?
- HTTP Headers
- Java VCS Deployment with Maven
- Setting Up Environment
- Share Environment
- Why is my environment in sleeping mode?
- Show all articles (9) Collapse Articles
-
Java
- Environment Variables - Java custom Environment Variables
- Java App server Configuration
- Java Options and Arguments
- Multiple Domains on Tomcat server
- Secure Java Encryption and Decryption
- Spring Boot Standalone and Clustered Java Applications with BitssCloud
- Timezone Data for Java/PHP App Server
- Tomcat HTTP to HTTPS redirect
- WildFly server
-
LiteSpeed Web Server
-
OOM Killer
-
Python
-
Reseller SetUp
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
-
Troubleshooting
-
Account Management
-
CDN
-
Databases
- Database Configuration
- Database Connection Strings
- Database Hosting in BitssCloud
- Environment Variables(Database)
- Galera Cluster not working
- How to export/Import Database via Command line
- How to install MSSQL server on Linux (2017)
- MariaDB/MySQL Auto-Сlustering
- MongoDB Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Replication
- PostgreSQL Master-Slave Cluster
- Remote Access to PostgreSQL
- Schedule Backups for MySQL and MariaDB Databases
- Scheduling Databases Backups
-
Domain Name Management
- Container Redeploy
- Custom Domain Name
- DNS Hostnames for Direct Connection to Containers
- How to Bind Custom Domain via A Record
- How to Bind Custom Domain via CNAME
- Multiple Custom Domains on an Nginx Web Server
- Multiple Domains with Public IP
- Multiple Public IP Addresses for a Single Container
- Setup WordPress Multisite Network with Domain Mapping and CDN
-
Jenkins
-
Load Balancing
-
PHP
- Creating Environment for PHP
- Deploy PHP Project Via GIT SVN
- How to Check Change PHP Version in BitssCloud
- How to create environment for AngularJs/ReactJs
- How to Enable PHP Extensions
- How to Install Custom PHP Application
- Ion cube Loader
- MariaDB PHP connection
- MySQL PHP Connection
- NGINX PHP
- PHP App Server Configuration
- PHP Connection to MongoDB
- PHP security settings
- PHP Session Clustering
- PostgreSQL PHP Connection
- Running Multiple Domain Names on Apache Server
- Security configuration for Apache
- Zero Downtime (ZDT) Deployment for PHP
- Show all articles (3) Collapse Articles
-
Release Notes
-
Ruby
-
SSH
-
Wordpress
-
Application Management
-
Cluster
-
Deploying Projects
-
Elastic VPS
- CentOS VPS
- Elastic VPS configuratation
- Elastic VPS with full root access
- Installation of cPanel in BitssCloud
- Java Console Application with CentOS VPS
- Linux VPS Access via Public IP
- Linux VPS Access via SSH Gate
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- SSH Access to VPS Gate
- Ubuntu VPS
- Ubuntu with CSF Firewall
-
High Availability
-
Jitsi
-
Node.js
-
Pricing System
-
Request Handling
-
Scaling
- Application Server with horizontal scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling: Multi Nodes
- Automatic Vertical Scaling
- Database Horizontal Scaling
- Docker Containers Horizontal Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
- Load Balancer with horizontal scaling
- Memcached horizontal scaling
- Storage Container
- VPS Horizontal Scaling
-
Traffic Distributor
-
General
- Apache & NGINX Modules
- BitssCloud Dashboard Guide
- Build and Deploy Hooks
- Cron Job scheduler
- FFMPEG Setup
- File Synchronization
- FTP Overview
- FTP/FTPS Support in BitssCloud
- How to Deploy Magento into BitssCloud PHP Cloud
- How to Enable Expert Mode in JCA
- How to open a support ticket to BitssCloud
- Installation of FTP
- Kubernetes Cluster
- MarketPlace
- Reduce Cloud Waste with Automatically Scheduled Hibernation
- Run Configuration
- SFTP Protocols for Accessing BitssCloud Containers.
- Supported OS Distributions for Docker Containers
- Timezone Addon
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Types of Accounts
- Varnish
- Websockets Support
- What is Cloudlet
- What is PaaS & CaaS
- WordPress AddOn
- Zero Code Change Deploy with No Vendor Lock-In for Smooth Migration across Cloud Platforms
- Show all articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
Go lang
-
Wordpress category
-
Data Storage Container
-
Memcached
-
Account & Pricing
PHP App Server Configuration
To perform the necessary configurations, press the Config button next to your application server. In the case, you have several application servers you can configure them together or separately. To do this follow the steps:
Open the drop-down menu at the top of the configuration tab. It includes the list of all of the app servers in your environment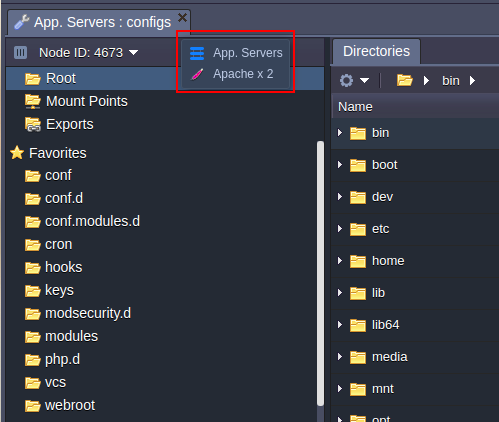
Choose the one you need and make the configurations.
- To apply the changes:
- only for the chosen server click Save only for the current instance button from drop-down menu;
- for all the servers click Save for all instances.
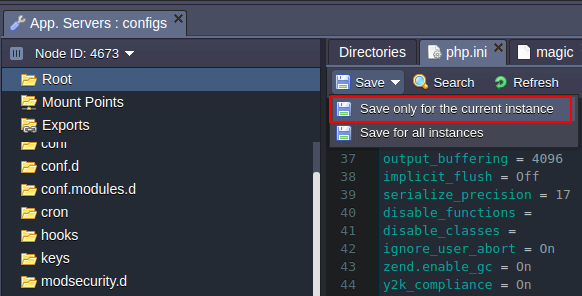
Note: if you create/rename a file or folder in the Configuration Manager, this will be applied only in the list of the chosen node. You can’t save this change for all of the app servers available in the environment. If you want to also create/rename the file or folder in the other servers you need to do this manually.
Below you can see the list of the configuration files available for editing in the PHP application servers:
- Apache
- NGINX-PHP
To get more information on which settings can be changed in the provided config folders, use the appropriate descriptions:
- etc
- conf
- conf.d
- webroot
- cron
- key
- modules
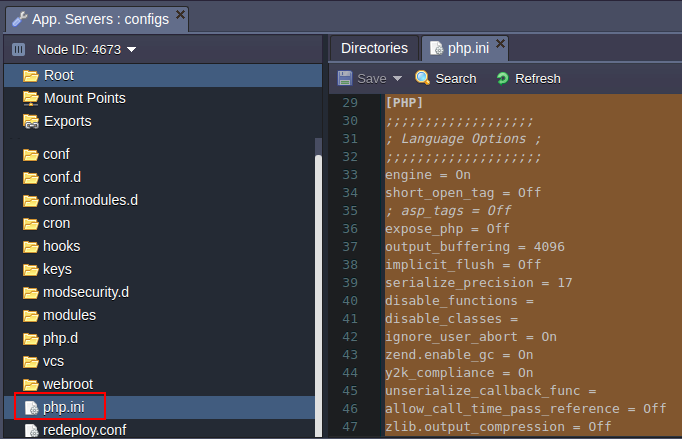
ETC
The main PHP server configurations are performed in the php.ini file which is located in the etc folder.
For example, here you can set the required:
- PHP extensions
- PHP accelerators
- Caching for NGINX-PHP
- Storing PHP sessions in Memcached
- PHP.INI Security Configurations
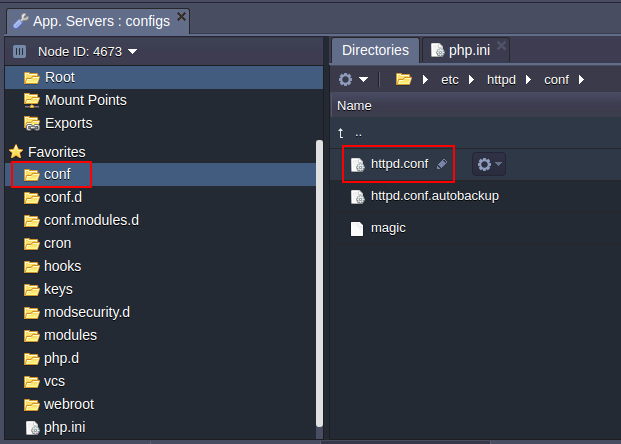
CONF
- For the Apache application server, the main configuration file is the httpd.conf located in the conf folder. For example, by using it, you can perform the following actions:
- set up Multiple Domains
- enable custom Apache modules
- use WebDav module
- perform necessary security configurations
- configure name-based virtual host
- enable statistics module to view your server’s statistics
| Note that if you change any configurations in httpd.conf file you need to delete the following string in order not to lose your custom settings while update: # autoconfiguration mark. |
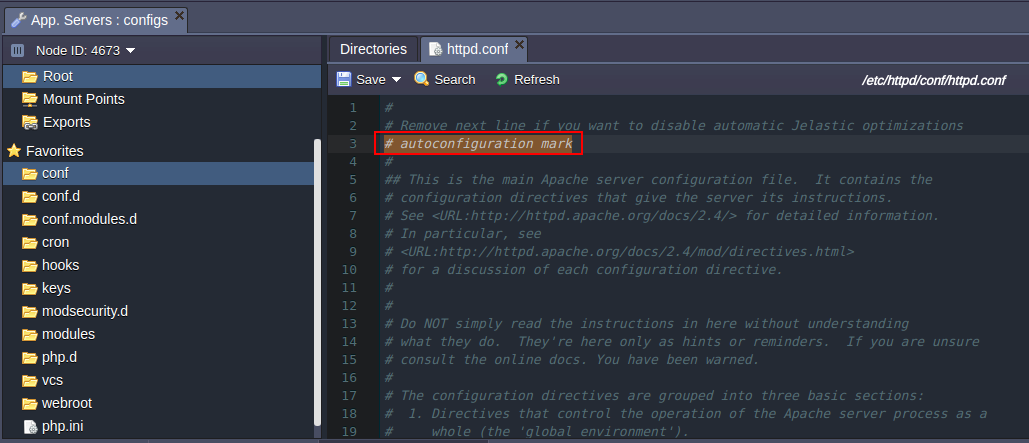
The number of workers for processing PHP requests is increased automatically in an Apache server depending on the cloudlet amount you stated for it.
To check this find and remember the MaxrRequestWorkers value (in httpd.conf file).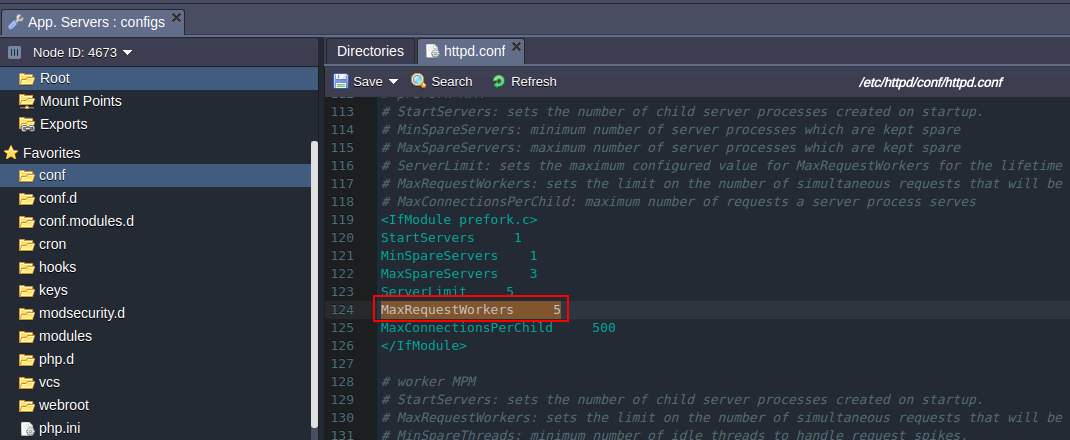
After that, change the topology of your environment by increasing or decreasing the cloudlet limit for your server.
Return to the conf > httpd.conf file. As you can see the number of MaxRequestWorkers has increased/decreased.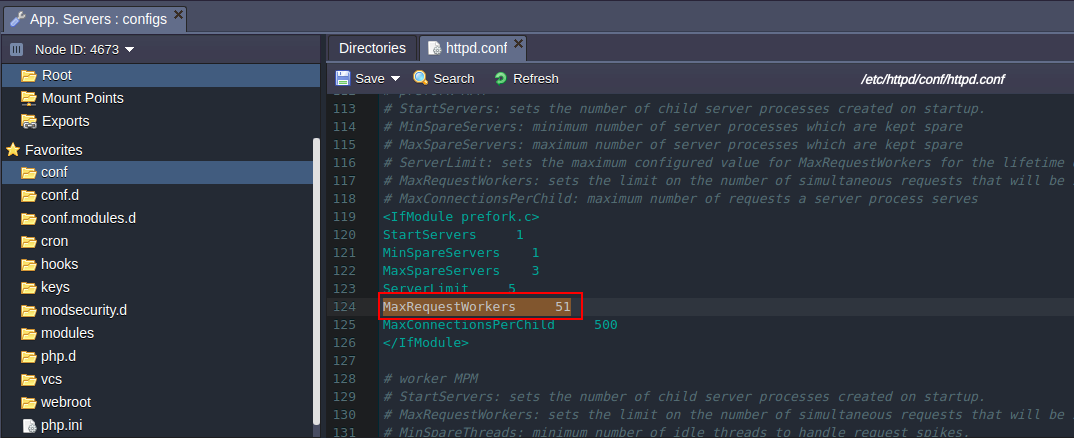
| Note that this function will be disabled if you remove the following string from the httpd.conf file: # autoconfiguration mark |
NGINX
For performing necessary configurations for an NGINX-PHP server the nginx.conf file, located in conf folder, is used. Use it to set up the following configurations:
- set up Multiple Domains
- use WebDav module
- perform necessary security configurations
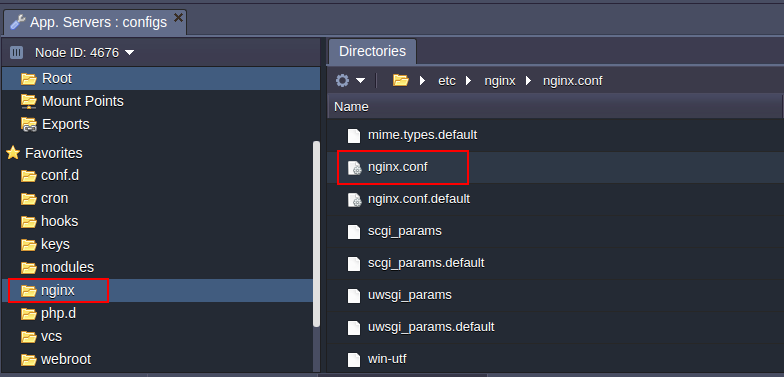
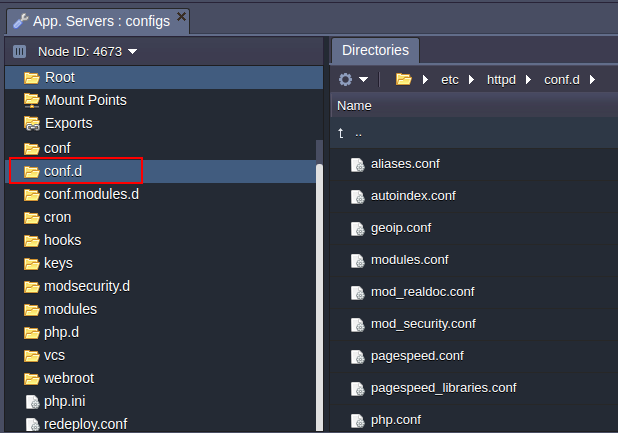
CONF.D
The conf.d folder is used for storing and managing sub configs.
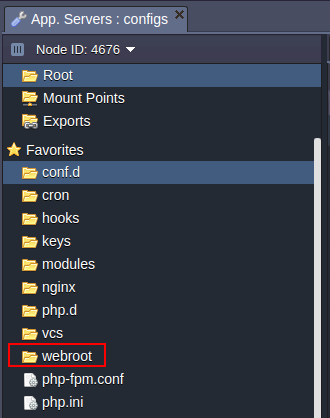
WEBROOT
The webroot folder is used for storing the unpacked application deployed to the environment.
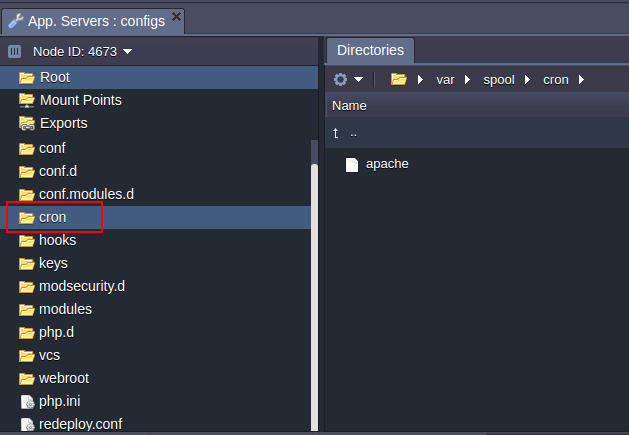
CRON
App servers include a cron folder with the config file where cronjobs can be configured.
Detailed information on Cronjob configuration can be found in the Setting Up a Cronjob document.
KEYS
The keys directory is used as a location for uploading any private key which is needed for your application.Generate the key, save it as a simple file and upload it to the key folder.
Now you can use it for different cases by simply stating the path to your key:
/var/lib/jelastic/keys/{key_file_name}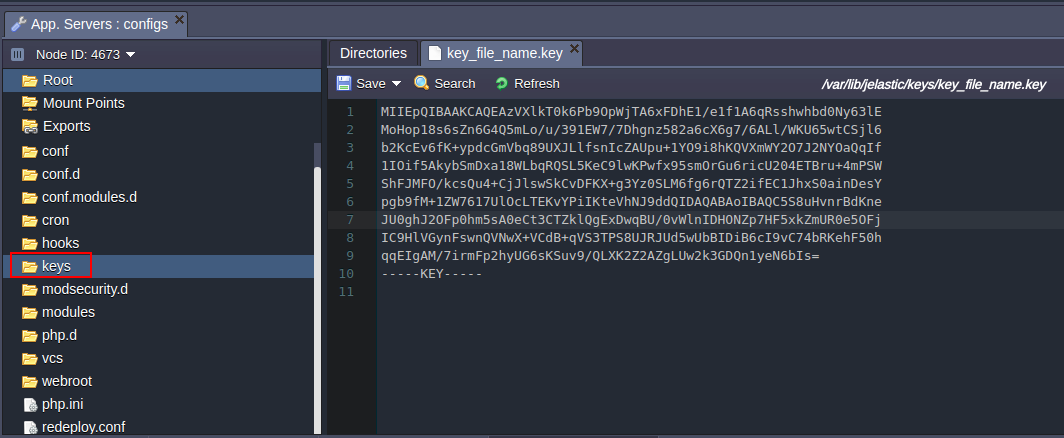
MODULES
The modules folder contains the php modules available in Jelastic by default. You can also upload your custom php modules to this folder, in order to activate them.
For more information navigate to the PHP Modules document.
Apache
| Folder | File | Path |
|---|---|---|
| etc | php.ini | /etc |
| conf.d | modules.conf aliases.conf geoip.conf mod_security.conf php.conf ssl.conf welcome.conf | /etc/httpd/conf.d/ |
| conf | httpd.conf | /etc/httpd/conf/ |
| webroot | /var/www/webroot | |
| cron | apache | /var/spool/cron |
| key | /var/lib/jelastic/keys | |
| modules | /usr/lib64/php/modules |
NGINX-PHP
| Folder | File | Path |
| etc | php-fpm.conf php.ini | /etc |
| conf.d | virtual.conf ssl.conf | /etc/nginx/conf.d |
| conf | nginx.conf | /etc/nginx |
| webroot | /var/www/webroot | |
| cron | nginx | /var/spool/cron |
| key | /var/lib/jelastic/keys | |
| modules | /usr/lib64/php/modules |
