-
.Net
-
Backup
-
Data Storage Containers
-
Docker Containers
-
Environment Management
- Swap-Domains
- Clone Environment
- Create Environment
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Aliases
- Environment Migration between Regions
- Environment Regions
- Environment Transferring
- Environment Variable
- Environment Variables
- Environment Variables(Apache meaven, Memcached)
- Environment Variables(Go)
- Environment Variables(JAVA)
- Environment Variables(Load Balancer)
- Environment Variables(Node.js)
- Environment Variables(PHP)
- Environment Variables(Ruby)
- How to Migrate a WordPress Site to BitssCloud PaaS
- How to migrate my environments from another Jelastic provider?
- HTTP Headers
- Java VCS Deployment with Maven
- Setting Up Environment
- Share Environment
- Why is my environment in sleeping mode?
- Show all articles (9) Collapse Articles
-
Java
- Environment Variables - Java custom Environment Variables
- Java App server Configuration
- Java Options and Arguments
- Multiple Domains on Tomcat server
- Secure Java Encryption and Decryption
- Spring Boot Standalone and Clustered Java Applications with BitssCloud
- Timezone Data for Java/PHP App Server
- Tomcat HTTP to HTTPS redirect
- WildFly server
-
LiteSpeed Web Server
-
OOM Killer
-
Python
-
Reseller SetUp
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
-
Troubleshooting
-
Account Management
-
CDN
-
Databases
- Database Configuration
- Database Connection Strings
- Database Hosting in BitssCloud
- Environment Variables(Database)
- Galera Cluster not working
- How to export/Import Database via Command line
- How to install MSSQL server on Linux (2017)
- MariaDB/MySQL Auto-Сlustering
- MongoDB Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Backups
- PostgreSQL Database Replication
- PostgreSQL Master-Slave Cluster
- Remote Access to PostgreSQL
- Schedule Backups for MySQL and MariaDB Databases
- Scheduling Databases Backups
-
Domain Name Management
- Container Redeploy
- Custom Domain Name
- DNS Hostnames for Direct Connection to Containers
- How to Bind Custom Domain via A Record
- How to Bind Custom Domain via CNAME
- Multiple Custom Domains on an Nginx Web Server
- Multiple Domains with Public IP
- Multiple Public IP Addresses for a Single Container
- Setup WordPress Multisite Network with Domain Mapping and CDN
-
Jenkins
-
Load Balancing
-
PHP
- Creating Environment for PHP
- Deploy PHP Project Via GIT SVN
- How to Check Change PHP Version in BitssCloud
- How to create environment for AngularJs/ReactJs
- How to Enable PHP Extensions
- How to Install Custom PHP Application
- Ion cube Loader
- MariaDB PHP connection
- MySQL PHP Connection
- NGINX PHP
- PHP App Server Configuration
- PHP Connection to MongoDB
- PHP security settings
- PHP Session Clustering
- PostgreSQL PHP Connection
- Running Multiple Domain Names on Apache Server
- Security configuration for Apache
- Zero Downtime (ZDT) Deployment for PHP
- Show all articles (3) Collapse Articles
-
Release Notes
-
Ruby
-
SSH
-
Wordpress
-
Application Management
-
Cluster
-
Deploying Projects
-
Elastic VPS
- CentOS VPS
- Elastic VPS configuratation
- Elastic VPS with full root access
- Installation of cPanel in BitssCloud
- Java Console Application with CentOS VPS
- Linux VPS Access via Public IP
- Linux VPS Access via SSH Gate
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- Setting Mail Server Inside CentOS VPS
- SSH Access to VPS Gate
- Ubuntu VPS
- Ubuntu with CSF Firewall
-
High Availability
-
Jitsi
-
Node.js
-
Pricing System
-
Request Handling
-
Scaling
- Application Server with horizontal scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling: Multi Nodes
- Automatic Vertical Scaling
- Database Horizontal Scaling
- Docker Containers Horizontal Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
- Load Balancer with horizontal scaling
- Memcached horizontal scaling
- Storage Container
- VPS Horizontal Scaling
-
Traffic Distributor
-
General
- Apache & NGINX Modules
- BitssCloud Dashboard Guide
- Build and Deploy Hooks
- Cron Job scheduler
- FFMPEG Setup
- File Synchronization
- FTP Overview
- FTP/FTPS Support in BitssCloud
- How to Deploy Magento into BitssCloud PHP Cloud
- How to Enable Expert Mode in JCA
- How to open a support ticket to BitssCloud
- Installation of FTP
- Kubernetes Cluster
- MarketPlace
- Reduce Cloud Waste with Automatically Scheduled Hibernation
- Run Configuration
- SFTP Protocols for Accessing BitssCloud Containers.
- Supported OS Distributions for Docker Containers
- Timezone Addon
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Types of Accounts
- Varnish
- Websockets Support
- What is Cloudlet
- What is PaaS & CaaS
- WordPress AddOn
- Zero Code Change Deploy with No Vendor Lock-In for Smooth Migration across Cloud Platforms
- Show all articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
Go lang
-
Wordpress category
-
Data Storage Container
-
Memcached
-
Account & Pricing
Volumes
The Volumes tab contains the list of mounted at the current container data volumes, which are designed to persist the data independently of the container lifecycle. They are displayed in a view of paths to the appropriate mounting points inside a node:
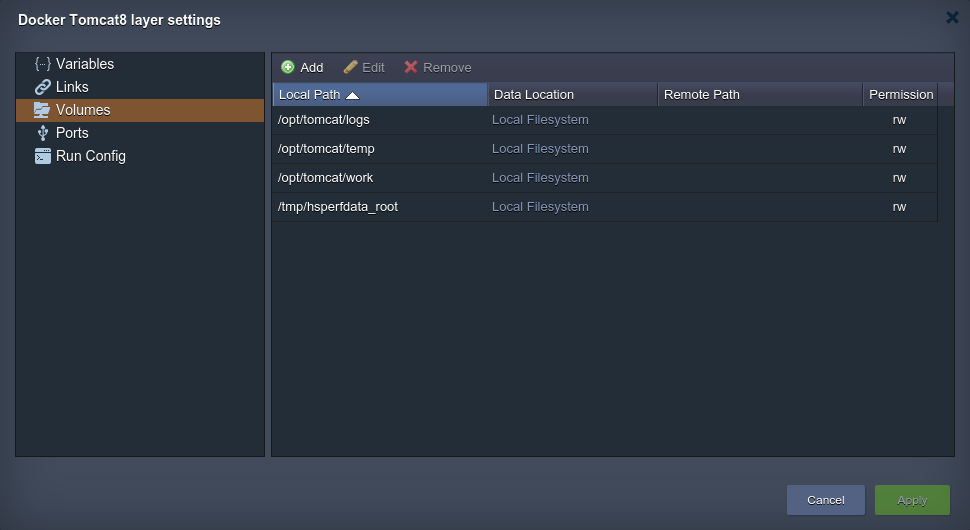
Storing data within volumes allows different internal operations (e.g. redeploying of the container with another tag version) to be performed without affecting or losing this data. To achieve such reliability, each volume’s content is packed into a separate .tar.gz archive for being automatically transferred out/in the container to the host physical server during this operation. This provides a high level of integrity for your data.
Below, we’ll consider how to add a custom volume for your Docker container and types of data mounting the BitssCloud Cloud provides – at a Local Filesystem, layer Master Container, separate dedicated Data Container, or External NFS Server.
Operating Custom Docker Volumes
By default, the predefined volumes (i.e. which are determined within the appropriate Docker template settings and are automatically set during container creation) are shown in the Docker layer settings > Volumes frame.
Besides that, you have the ability to mount and manage your custom volumes, placed either locally, at other instances on a Platform, or on any external server. For that, follow the steps below.1. Select the Add button above the list to see four tabs, named in accordance with the types of volumes you are able to create:
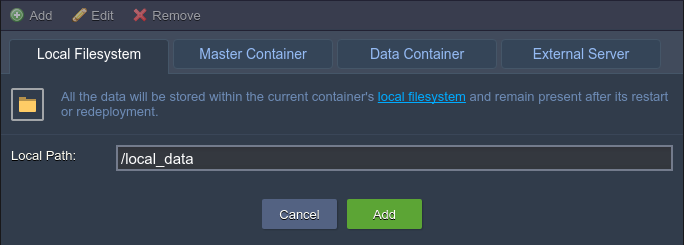
Local Filesystem – the specified directory will be used as local storage, intended to persist the data independently of the current container lifecycle (as well as by any other node)
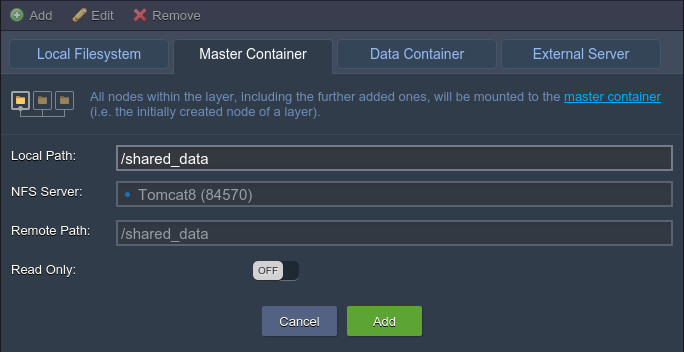
Master Container – data, stored within such volume, is physically placed at the initially created node of the layer (so-called “master node”) and is automatically shared with all of the rest instances within this layer
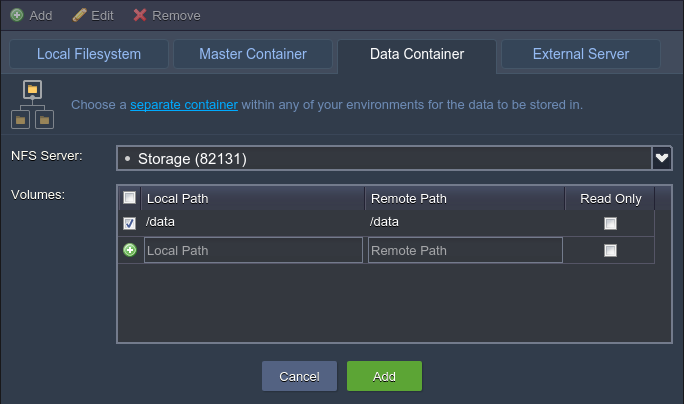
Data Container – this type of volume allows mounting data from the special dedicated Data Storage server, that belongs to one of the environments of your BitssCloud account
External Server – this option is intended to mount data from the external NFS server (either your custom third-party storage or BitssCloud container at another platform)
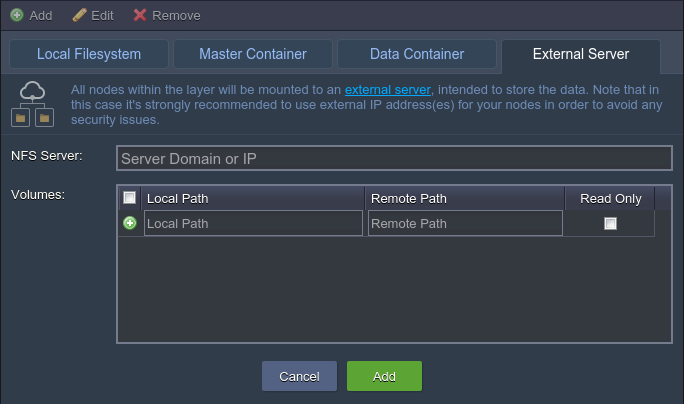
When all the parameters for the chosen mount type are specified (the details can be observed within the linked guides), click Add to finish the configuration.
2. With the Edit option at the top pane (or through double-clicking on the corresponding record), you can change some settings for the already existing volumes:
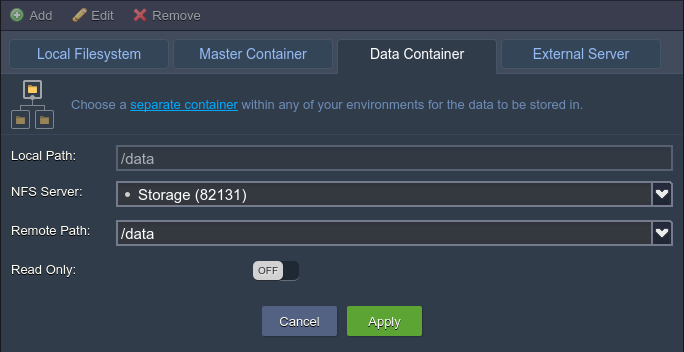
Here, the Local Path is an unchangeable value, but you still can switch the mounting method (by moving to a different tab) and/or adjust the access permissions (with the Read-Only switcher).
Do not forget to apply the changes you’ve made.
3. In case your custom volume is not needed anymore, it can be easily unmounted by choosing the corresponding string and clicking on the Remove button above.
Note:
- before deletion, make sure the appropriate volume does not contain any substantial data, as it will be permanently removed
- the predefined (i.e. default) volumes can’t be deleted (whilst still being available for editing)
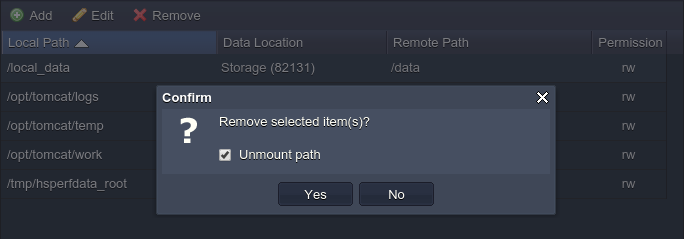
Confirm your decision within the appeared pop-up frame.
After that, don’t forget to apply all your changes with the corresponding button at the general Docker layer settings window and, if required, within the topology wizard (in case of modifying the already existing environment).
